9 common side effects of periods

Periods are a part of the monthly menstrual cycle for people with a uterus. It is the shedding of the uterine lining in the form of blood and other fluids and tissue that may last for 3-7 days. Approximately 5 days to 2 weeks before its arrival, 90% of people who menstruate may feel certain symptoms. This is collectively known as premenstrual syndrome (PMS). Some of the most common side effects or symptoms of periods include:
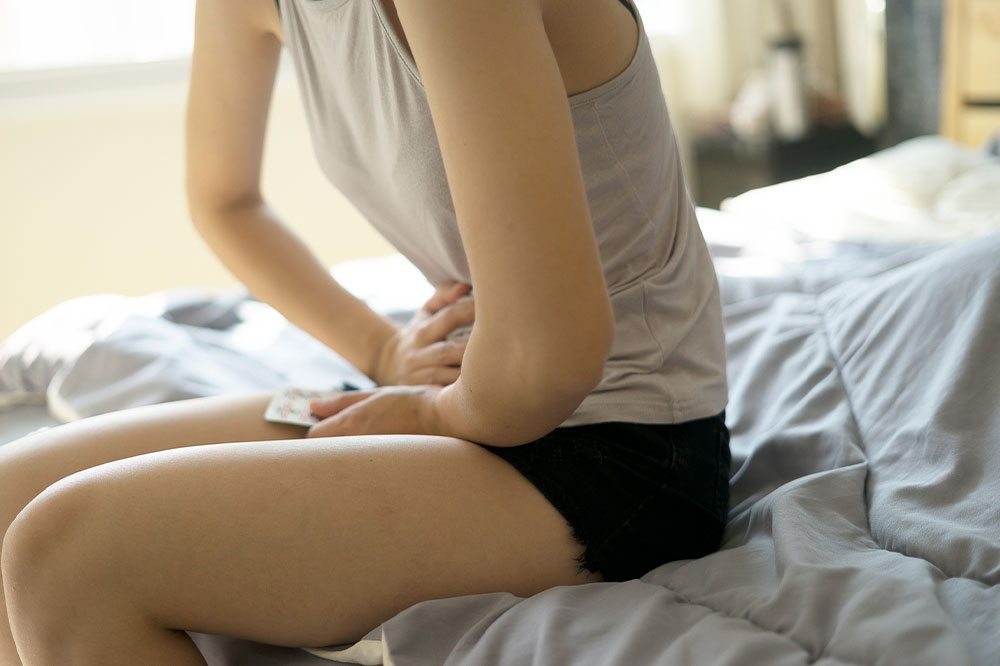
Abdominal cramps
Menstrual cramps, also known as primary dysmenorrhea, cause an achy or cramping feeling in the lower abdomen, lower back, and upper thighs. Their severity may range from dull or mild discomfort to severe pain that interferes with one’s daily activities. People with conditions like endometriosis, cervical stenosis, adenomyosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and fibroids may experience worse cramps during their menstrual cycle.
Gas and bloating
Some people also experience a sensation of heaviness in the stomach or may struggle to zip up their pants. This is also known as bloating and is caused due to changing hormone levels which lead to higher retention of water in the body. For most people, the worst bloating occurs on the day their period begins. The body’s hormonal changes also impact bowel functioning and can lead to gas, diarrhea, constipation, or nausea.
Breakouts
During one’s menstrual cycle, the body undergoes various hormonal changes. When no pregnancy occurs during ovulation, estrogen and progesterone levels decline while testosterone levels increase slightly. These changes stimulate sebum production and can lead to breakouts on the face, back, and other areas of the body, a week before one’s period starts.
Mouth issues
The fluctuation in one’s estrogen and progesterone levels also impacts the mouth, increasing sensitivity and causing gum irritation. These can also lead to swollen, bright red gums, canker sore development, bleeding gums, or gingivitis.
Tender breasts
During the ovulation phase (about halfway through the menstrual cycle), progesterone levels start to rise in the body, and can cause swelling in the mammary glands in the breasts. This can result in the sensation of tender breasts just before or during one’s period.
Headache
Changes in hormone levels like estrogen and progesterone can also impact the production of other hormones such as cortisol and serotonin. For example, a fluctuation in serotonin levels can instigate a migraine headache during ovulation, or the headache can occur before, during, or immediately after one’s period.
Mood swings
Fluctuating hormone levels can also cause mood changes like depression, irritability, or anxiety. This is because changes in estrogen production also cause fluctuations in serotonin, the feel-good hormone.
Yeast infections
Another common occurrence during the menstrual cycle is changes in vaginal pH levels. These changes can disrupt the balance of yeast and bacteria in the nether region and make one more susceptible to yeast infections. However, mild yeast infections tend to resolve themselves in a few days without treatment. If it lasts for longer than two or three days or occurs frequently, it may be time to consult a gynecologist.
Fatigue
Just before one’s period, there are significant changes in the hormones, which can impact energy levels as well, causing tiredness or fatigue. Some people may also experience trouble sleeping due to other PMS symptoms, which can impact their energy levels during the day.