Causes, symptoms, and remedies for herpes

Herpes is a common viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It manifests in two primary types: HSV-1, known as oral herpes or cold sores, and HSV-2, responsible for genital herpes. According to the CDC, reports estimated 572,000 new cases of genital herpes each year in the country and oral herpes in 50% to 80% of the adult population. There is no cure; an individual can only manage the condition once it’s contracted.
Causes of herpes
Viral transmission
The transmission of herpes occurs through direct contact with the infected skin or mucous membranes. It is important to note that the virus can be transmitted even when the infected person is not experiencing visible symptoms. This emphasizes the need for caution and preventive measures.
Asymptomatic shedding
Asymptomatic shedding is a phenomenon where the virus is shed from the skin or mucous membranes of an infected individual, even when no visible symptoms are present. This can happen intermittently, increasing the risk of transmission. Heightened awareness and preventive practices are crucial to reducing transmission rates. At present, asymptomatic shedding is a fairly common mode of herpes transmission, as most individuals don’t notice that they have the infection.
Symptoms of herpes
Primary infection
The initial outbreak of the herpes virus is considered to be the most severe. The blisters or sores are known to be painful. In addition to that, individuals may also experience flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, and muscle aches. Some might even experience the presence of swollen lymph nodes. These symptoms can be distressing and may require a doctor’s attention for effective management.
Recurrent outbreaks
After the primary infection has taken place, the virus establishes a latent state within cells. Patients might experience periodic reactivation, resulting in possible frequent recurrence of the infectious outbreaks. Triggers for these recurrences may include physical or emotional stress, illness, hormonal changes, or exposure to sunlight.
Physical discomfort
Before the visible symptoms appear, individuals may experience localized sensations like itching, burning, or tingling. Discomfort associated with these symptoms can indicate an impending outbreak and serve as signals for individuals to take preventive measures.
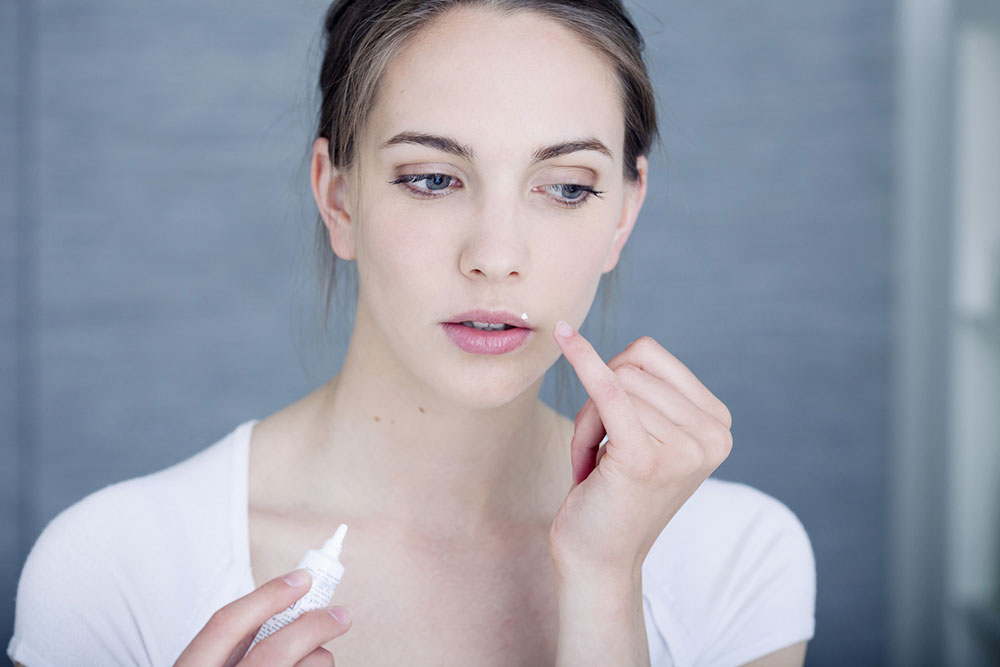
Blisters and sores
Blisters and sores are hallmark symptoms of herpes outbreaks. As the outbreak develops into a painful event, fluid-filled blisters or open sores occur. These lesions can occur in various locations, but the mouth and genital area are fairly common. The discomfort associated with these blisters can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life during an outbreak.
Treatments
Healthcare treatment
Herpes-associated blisters often resolve on their own without any treatment. However, if there is a severe outbreak or the patient is frequently dealing with painful blisters and sores, it is advisable to seek treatment from a doctor.
Maintaining personal hygiene
Practicing good personal hygiene is a fundamental aspect of herpes management. Regular handwashing and keeping affected areas clean helps prevent the spread of the virus.
Managing stress
Stress reduction techniques play a pivotal role in managing herpes outbreaks. Engaging in activities such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can help lower stress levels and reduce the frequency of recurrent outbreaks.
Avoiding triggers
Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is crucial. These may include specific foods, excessive sun exposure, hormonal fluctuations, or periods of emotional stress. Understanding and managing triggers can significantly reduce the occurrence of outbreaks.